Al-Jazeera reports
Washington, DC – US legislation threatening to sanction Qatar for its support of “Palestinian terror” was sponsored by 10 lawmakers who received more than $1m over the last 18 months from lobbyists and groups linked to Israel, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
The bill was introduced to the US House of Representatives on May 25, but the text wasn’t available until Friday morning, hours after Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Egypt put 59 people and 12 institutions linked to Qatar on a “terror list”.
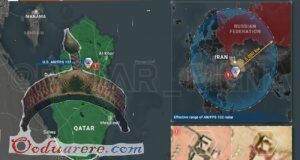
The nations abruptly ended diplomatic relations with Qatar on Monday, accusing Doha of supporting “extremism” and siding with their regional rival Iran.
“Hamas has received significant financial and military support from Qatar,” the Palestinian International Terrorism Support Prevention Act of 2017, also known as HR 2712, said. It went on to list sanctions including an end of exports of defence technologies, arms, and loans or financing totalling more than $10m.
For Trita Parsi, author and founder of the National Iranian American Council (NIAC), a nonprofit that aims to strengthen the voice of US citizens of Iranian descent, the similarities between the US-allied Arab nations’ “terror list” and HR 2712 show growing cooperation between Gulf Arab states and Israel.
“The coordination between hawkish pro-Israel groups and UAE and Saudi Arabia has been going on for quite some time,” Parsi told Al Jazeera. What is new, he continued, is pro-Israel groups such as the Foundation for Defense of Democracies “coming out with pro-Saudi [articles] and lobbying for them on Capitol Hill”.
Israel, Egypt and Saudi Arabia all view the Muslim Brotherhood, an Islamist political group, as a threat. Deposed Egyptian president Mohammed Morsi belonged to the group, which endured a heavy-handed crackdown in Egypt since a military coup installed Abdel Fatah el-Sisi as president in 2014.
The Brotherhood was the ideological base for Hamas, the Islamist rulers of the besieged Gaza Strip that have fought three wars with the Israelis. The Saudis demand that Qatar stop supporting the Muslim Brotherhood and Hamas in a move that aligns with Egyptian and Israeli policy.
Israel’s influence on US policymakers is clear. HR 2712’s sponsors received donations totaling $1,009,796 from pro-Israel individuals and groups for the 2016 election cycle alone, according data collected by the Center for Responsive Politics, an independent research group tracking money in US politics and its effect on elections and public policy, and then compiled by Al Jazeera.
“They’re not traditional pro-Saudi lawmakers. They’re in the pro-Likud camp,” Parsi said, referring to the party of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu.
The bill has bipartisan sponsorship. Five of the lawmakers come from the House Committee on Foreign Relations (HCFR), including sponsor Brian Mast, a first-term Republican congressman from Florida, and Ed Royce and Eliot Engel, the ranking Republican and Democrat of the HCFR, respectively.
Royce received $242,143 from pro-Israel sources for the 2016 election cycle, $190,150 went to Engel. Mast, who volunteered with the Israeli military after he finished serving in the US Army, received $90,178.
Ileana Ros-Lehtinen, a Florida Republican, received $150,300 in 2016, pushing her 27-year career total of pro-Israel dollars to more than $1m.
In contrast with the $1 million donated by pro-Israel entities in 2016, HR 2712’s sponsors received roughly $25,700 in donations by pro-Saudi and UAE lobbying groups over the last 18 months, according to filings with the US Department of Justice made public under the Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA).
The act requires that lobbyists track and submit donations and contacts between themselves and lawmakers when working for foreign governments.
Al Jazeera’s investigation covered 10 firms associated with Saudi and Emirati lobbying efforts. However, these are not exhaustive. Both Gulf nations have rapidly expanded their lobbying in recent years and could include further donations from individuals.
FARA filings also document frequent emails and meetings between the 10 lawmakers and Saudi-UAE lobbyists, as well as calls to major media outlets concerning news coverage of major events.
Texas Republican Ted Poe, who said in a release he was proud to support HR 2712 because it “will make countries like Qatar, Iran, and others pay a price for their support for terrorism” was the only legislator who does not have a record of any donations from lobbyists linked to Israel, Saudi or UAE.
Al Jazeera’s requests for comment from several sponsors, including Brian Mast and the HCFR, were not immediately answered.
Regarding the increased collaboration between the Gulf nations and Israel, which recently entered its 50th year of occupying Palestine, Parsi said even though there are disagreements they share a common goal.
“To use the opportunity they have with the Trump administration to restore an order in the region that is appealing to them – an order based on Iran’s isolation and the re-prioritisation of Saudi Arabia, Egypt and Israel,” he said.
The previous Obama administration shook the status quo of the Middle East by making the landmark nuclear deal with Iran that eased sanctions and allowed for the Shia regional power to continue researching nuclear power. The agreement was based on an end to Iran’s efforts to develop nuclear weapons, and it has complied with the terms such as intermittent inspections by international agencies.
Obama famously said the Saudis need to find “an effective way to share the neighbourhood and institute some sort of cold peace” with the Iranians.
“But then Obama okayed billion dollar arms deals to assure Gulf partners he wasn’t entirely pivoting towards Iran,” William Hartung, director of the Arms & Security Project at the Center for International Policy, a think-tank in Washington, DC, told Al Jazeera.
Now, Trump has adopted an “all-in” approach to Saudi relations, including a controversial $110bn arms deal regardless of human rights concerns surrounding the use of these weapons in the ongoing Yemen conflict.
Arms sales have long acted as a means of influencing US policy. “There was always a sort of tacit quid pro quo,” Hartung continued. The Saudis would buy US weapons and receive the superpower’s protection, the arms expert explained.
Israel has historically raised concerns about arms deals with Gulf Arab states, who last fought a war in 1973. But the Israeli leadership has “kept quiet” about the $110bn arms deal with Saudi Arabia inked by the Trump administration because “there was a shift from viewing the Saudis as a potential adversary”, Hartung said, because Iran is a common enemy.
“In the old days, there was a pro-Israel block in Congress … that would have been very sceptical and possibly pushed for votes against arms sales to Saudi Arabia. That hasn’t happened in a long time,” he said.
The geographic and corresponding congressional re-alignment will continue, Parsi predicted, and pressure on Qatar will remain.
The small Gulf country “is a problem because it is independent and doesn’t share Saudi Arabia’s obsession with Iran”, he said.
For its part, Qatar has vowed to retain its independence.
 Ọmọ Oòduà Naija Gist | News From Nigeria | Entertainment gist Nigeria|Networking|News.. Visit for Nigeria breaking news , Nigerian Movies , Naija music , Jobs In Nigeria , Naija News , Nollywood, Gist and more
Ọmọ Oòduà Naija Gist | News From Nigeria | Entertainment gist Nigeria|Networking|News.. Visit for Nigeria breaking news , Nigerian Movies , Naija music , Jobs In Nigeria , Naija News , Nollywood, Gist and more